Have you ever wondered about the substance known as ketamine? It's a topic that comes up quite a bit, so, you know, many people are curious about what it really is. This compound has a rather interesting and somewhat complex story, playing different roles in medicine and, unfortunately, sometimes outside of medical settings. Getting a clear picture of ketamine means looking at its effects, how it's used, and the things that make it a serious subject for discussion.
For a long time, ketamine has been a valuable tool in hospitals and clinics, especially for certain medical procedures. It's a type of medication that can bring about a unique state, helping people feel less pain and sometimes even forget what's happening around them during a procedure. Yet, it's also a substance that, when used without proper guidance, can lead to some very serious health concerns, including the possibility of developing a drug use disorder. This is something the World Health Organization (WHO) and other health bodies talk about quite a lot, actually.
So, understanding what drug ketamine truly is means looking beyond just a simple definition. It means exploring its medical applications, its potential for misuse, and the broader implications for public health. We will go into what makes ketamine distinct, what its different forms are, and why it matters to know about this substance, really.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is Ketamine?
- How Ketamine Works in the Body
- Medical Uses of Ketamine
- Ketamine in Anesthesia
- Emerging Mental Health Treatments
- Ketamine as a Recreational Drug
- Short-Term Effects of Misuse
- Long-Term Risks and Concerns
- Understanding Drug Use Disorders
- Legal Status and Regulation
- Frequently Asked Questions About Ketamine
- Is ketamine a psychedelic?
- What does ketamine do to your brain?
- Is ketamine addictive?
- Seeking Help and Further Information
What Exactly Is Ketamine?
Ketamine, you know, is a dissociative anesthetic. That's a fancy way of saying it makes you feel disconnected from your pain and surroundings, even your own body. It was first made back in the 1960s, and doctors quickly found it very helpful for medical procedures. It's listed in what's called the anatomical therapeutic chemical (ATC) classification system, which groups active substances based on what part of the body they affect and how they work. This system, so, helps medical professionals categorize and understand different medicines.
Basically, ketamine is a psychoactive drug. This means it affects the brain and can change how you feel, think, and act. The World Health Organization (WHO) often provides information on psychoactive drugs, including a lexicon of alcohol and drug terms that gives clear definitions for many words used in this field. It's a substance that, in some ways, stands out because of its particular effects, which are quite distinct from other types of medications, actually.
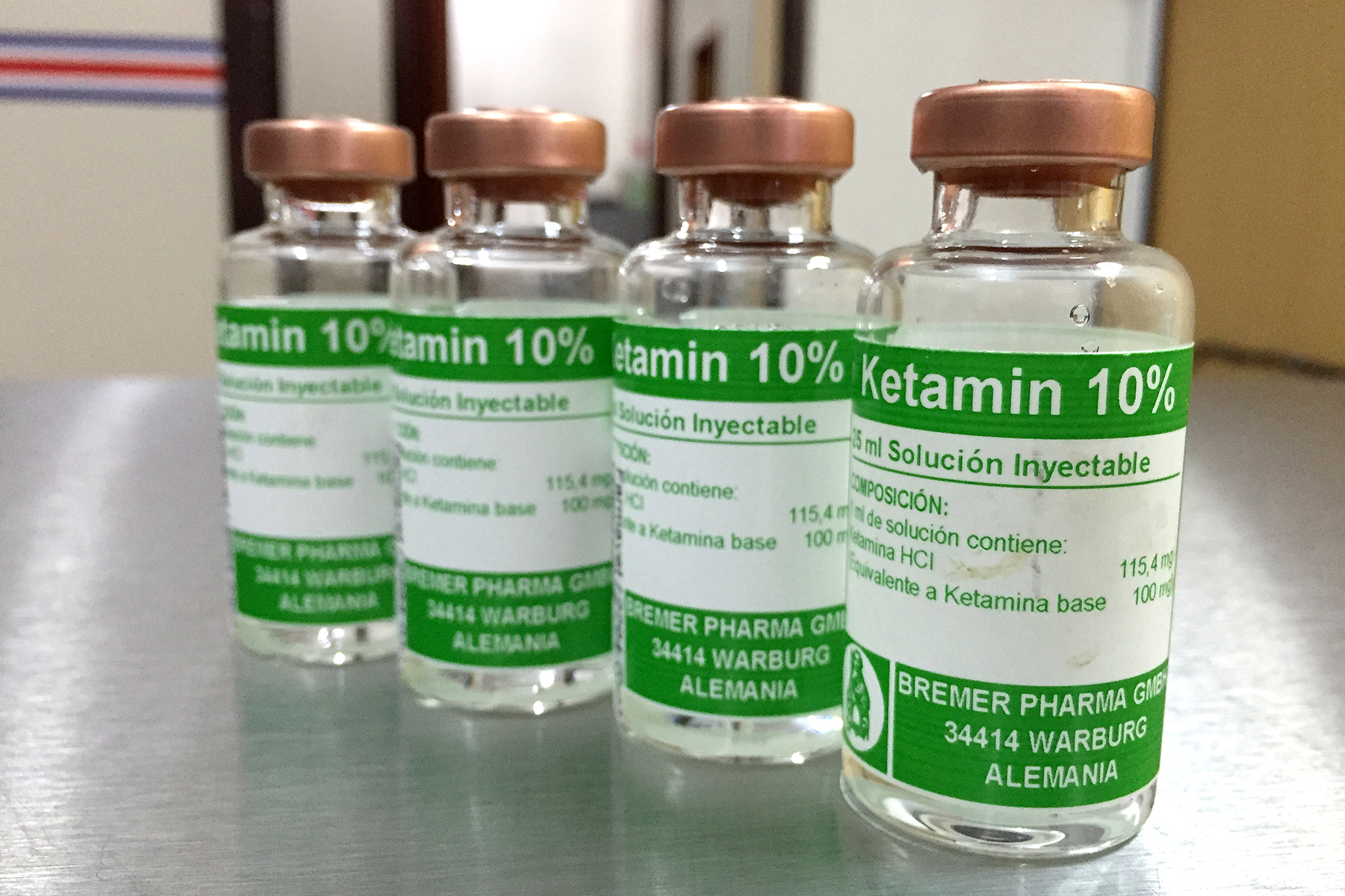
You might find ketamine as a clear liquid, which is typically for injection, or sometimes as a white powder. The powder form is often what people encounter when it's used without medical supervision, and that's where many of the risks come in, obviously. The way it looks and is used can vary, but its core chemical makeup is what gives it its specific properties, you know.
How Ketamine Works in the Body
When someone takes ketamine, it quickly gets into the brain. It works by blocking certain receptors in the brain, especially one called the NMDA receptor. This action, so, helps to reduce pain signals and can also create that feeling of detachment. It's a rather quick process, which is why it's been so useful in emergency medicine and for fast-acting procedures, you know.
The effects of ketamine can be quite immediate, and they depend a lot on the amount taken. A small dose might make someone feel a bit dreamy or confused, while a larger amount can lead to a much deeper state of dissociation, where a person might not respond to their surroundings at all. This difference in effect based on dose is a key aspect of how it's managed in a medical setting, and also why it's so risky outside of one, you know.
It's important to remember that, like many substances that affect the brain, ketamine changes how brain cells communicate. This can lead to altered perceptions, changes in mood, and even memory issues, especially with higher doses. The way it interacts with brain chemistry is what gives it its powerful, yet sometimes unpredictable, impact, you know.
Medical Uses of Ketamine
For decades, ketamine has been a very important medicine in hospitals all over the world. Its ability to provide pain relief and sedation quickly has made it a go-to choice for doctors in many situations. Access to appropriate medications, like ketamine, is shown to have substantial impacts on community health and related economic indicators, so it's a valuable tool when used correctly.
Ketamine in Anesthesia
One of the main ways ketamine is used is as an anesthetic. It's often chosen for procedures where a person needs to remain stable, like in emergency situations or on battlefields, because it generally doesn't suppress breathing or blood pressure as much as some other anesthetics. This makes it a safer option for people who might be in a fragile state, which is pretty important, actually.
Doctors use it for short operations, setting broken bones, or even for pain relief in serious injuries. It allows patients to be calm and pain-free without needing a lot of complex equipment to support their breathing. This versatility, you know, makes it a valuable part of a doctor's toolkit, especially when other options might be too risky or unavailable.
Emerging Mental Health Treatments
More recently, there's been a lot of interest in ketamine for treating certain mental health conditions, especially severe depression that hasn't responded to other treatments. It's given in much smaller doses than for anesthesia, and always under very strict medical supervision. This new application is quite different from its traditional use, but it's showing some real promise for people who have struggled for a long time, apparently.
Studies are looking into how ketamine might help reset brain pathways that are involved in mood disorders. It's not a quick fix, and it's certainly not something someone should try on their own. The medical community is carefully developing guidelines for its use in this area, which is a rather big step for mental health care, you know. For example, the WHO announces development of updated guidelines for psychosocially assisted pharmacological treatment of opioid dependence and community management of opioid, which shows their commitment to proper medical use of such substances.
Ketamine as a Recreational Drug
Despite its important medical uses, ketamine is also, unfortunately, used recreationally. The use of psychoactive drugs without medical supervision is associated with significant health risks and can lead to the development of drug use disorders. When people use ketamine outside of a controlled medical environment, they often take unpredictable amounts, which makes the experience very dangerous, obviously.
It's sometimes called "Special K" or "K" on the street. People might snort it as a powder, or sometimes even inject it. The effects can be quite intense and vary wildly from person to person, and from dose to dose. This unpredictability is a major part of the danger, you know.
Short-Term Effects of Misuse
When someone misuses ketamine, the immediate effects can range from feeling detached and dreamy to experiencing hallucinations. People might feel like they are floating or having an out-of-body experience. This is often referred to as entering a "K-hole" at higher doses, which can be a very frightening and disorienting experience, apparently.
Other short-term effects can include confusion, slurred speech, problems with coordination, and even temporary paralysis. It can also cause a rapid heart rate and high blood pressure, which can be particularly risky for some people. These effects can make someone very vulnerable, putting them at risk of accidents or injuries, you know, because they aren't fully aware of their surroundings or able to control their body.
Long-Term Risks and Concerns
Using ketamine over a long period, especially recreationally, comes with some very serious health problems. One of the most well-known and concerning issues is damage to the bladder, sometimes called "ketamine bladder." This can lead to severe pain, frequent urination, and, in some cases, permanent kidney damage, which is pretty awful, actually.
There are also concerns about its impact on the brain over time. Chronic misuse can lead to memory problems, difficulties with thinking clearly, and even psychological dependence. People might develop a strong craving for the drug, making it very hard to stop using it. The WHO provides a lexicon of alcohol and drug terms, which helps to define conditions like "drug use disorders" that can develop from such misuse, you know.
Understanding Drug Use Disorders
When someone uses psychoactive drugs without medical supervision, there's a real risk of developing what's known as a drug use disorder. This isn't just about using a substance sometimes; it's about a pattern of use that leads to significant problems in a person's life. It can affect their health, their relationships, and their ability to function at work or school, you know.
The World Health Organization (WHO) regularly puts out reports and guidelines on substance use. For instance, a new report from the WHO highlights that 2.6 million deaths per year were attributable to alcohol consumption, accounting for 4.7% of all deaths. While this report focuses on alcohol, it underscores the broad impact of psychoactive substances on public health. The principles of understanding and addressing substance use disorders apply to many different drugs, including ketamine, obviously.
Recognizing the signs of a drug use disorder is a very important step. These signs might include needing more of the drug to get the same effect, trying to cut down but not being able to, spending a lot of time getting or using the drug, or continuing to use it even when it causes problems. Support and treatment are available for those who need it, and that's a very important message to share, you know.
Legal Status and Regulation
Because ketamine has legitimate medical uses but also a high potential for misuse, its legal status is pretty tightly controlled in most places. In many countries, it's classified as a controlled substance, which means it's illegal to possess or distribute it without a proper medical license or prescription. This regulation is in place to try and prevent harm and ensure it's only used safely, you know.
The regulations also cover how it's manufactured, stored, and prescribed. These rules are put in place to protect public health and to make sure that such a powerful drug is handled with the utmost care. About WHO drug information, which is a quarterly journal, it provides an overview of topics relating to medicines development and regulation, which is targeted to a wide audience. This kind of information helps guide countries in setting their own rules for substances like ketamine, you know.
Breaking these laws can lead to serious penalties, including fines and jail time. The strict controls reflect the serious risks associated with ketamine when it's not used under professional medical guidance. It's a clear message about the dangers of unsupervised use, really.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ketamine
People often have a lot of questions about ketamine, especially given its varied uses and public perception. Here are some common inquiries.
Is ketamine a psychedelic?
While ketamine can cause hallucinations and altered perceptions, it's technically classified as a dissociative anesthetic, not a classic psychedelic. Psychedelics, like LSD or psilocybin, typically work on serotonin receptors and produce different types of experiences. Ketamine, on the other hand, primarily works on NMDA receptors, causing that feeling of detachment. So, while there's some overlap in effects, their mechanisms are distinct, you know.
What does ketamine do to your brain?
Ketamine primarily blocks NMDA receptors in the brain, which are involved in learning, memory, and pain processing. By blocking these, it can reduce pain, create a feeling of detachment, and even affect mood pathways. At higher doses, it can disrupt normal brain communication, leading to confusion, memory loss, and a disconnect from reality. Its effects on the brain are quite profound, really, and vary significantly with the dose, you know.
Is ketamine addictive?
Yes, ketamine can be addictive, especially with repeated recreational use. People can develop both a psychological and physical dependence on it. The psychological craving can be very strong, leading individuals to seek out the drug compulsively despite negative consequences. Over time, the body can also adapt to its presence, leading to withdrawal symptoms if use is stopped suddenly. This is why medical supervision is so important when it's used therapeutically, you know.
Seeking Help and Further Information
Understanding what drug ketamine is, including its medical uses and the serious risks of misuse, is very important for everyone. If you or someone you know is struggling with substance use, remember that help is available. There are many resources and people who want to support you in finding a path to wellness. You can learn more about substance use and recovery on our site, or even check out this page for more detailed information on support services that can make a real difference.
Access to appropriate medications and proper care, like that described in guidelines for treatment and care, consolidating all previous guidelines into a single resource, is essential for positive health outcomes. It's about getting the right information and support when you need it most, you know.


Detail Author:
- Name : Eleanora Welch II
- Username : cummings.camron
- Email : jones.cordelia@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1996-10-25
- Address : 116 Payton Loaf Waylonfurt, SD 70319
- Phone : 301-872-3402
- Company : Feil Group
- Job : Concierge
- Bio : Blanditiis velit asperiores nemo dicta. Eius corrupti eius ut est est. Perspiciatis quisquam enim distinctio aut explicabo eaque. Veniam eveniet ut dicta nobis facere asperiores.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/viola_ortiz
- username : viola_ortiz
- bio : Aperiam mollitia adipisci impedit ducimus non.
- followers : 2956
- following : 748
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/viola.ortiz
- username : viola.ortiz
- bio : Omnis labore ducimus harum accusamus ipsam.
- followers : 5933
- following : 512
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/viola_ortiz
- username : viola_ortiz
- bio : Eum quam soluta ab nihil. Laboriosam iusto deleniti dolores in unde.
- followers : 5142
- following : 1602
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/viola_ortiz
- username : viola_ortiz
- bio : Libero aut et ut laboriosam. Nobis asperiores cum et porro.
- followers : 3539
- following : 369
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@viola8804
- username : viola8804
- bio : Officiis dolor aspernatur possimus optio id officia.
- followers : 1915
- following : 1681

